Psyllium Husk Contraindications | Who Should Avoid It and Why – 2026

While psyllium husk offers remarkable health benefits for most people, understanding psyllium husk contraindications is critical for safety. Certain medical conditions, medications, and individual circumstances make psyllium use inadvisable or require special precautions. Psyllium husk contraindications aren’t about the fiber being inherently dangerous – it’s about specific situations where the risk outweighs benefits or where psyllium interferes with necessary medical treatments. Some people experience serious complications from psyllium due to swallowing disorders, intestinal obstructions, or medication interactions that reduce drug effectiveness.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain all psyllium husk contraindications clearly: absolute contraindications where you should never use psyllium, relative contraindications requiring medical supervision, medication interactions affecting drug absorption, special populations needing caution, warning signs that indicate you should stop using psyllium, and how to safely navigate these concerns with your healthcare provider.
What Are Psyllium Husk Contraindications?
Contraindications are specific situations where a substance, supplement, or medication should not be used because it could cause harm.
Absolute vs Relative Contraindications
Absolute contraindications:
Conditions where psyllium should never be used under any circumstances. The risks are too severe.
Relative contraindications:
Situations requiring medical supervision or special precautions. Psyllium might be used cautiously with proper oversight.
Understanding this distinction helps you make informed decisions about whether psyllium is appropriate for your situation.
Absolute Psyllium Husk Contraindications
These are the non-negotiable situations where you should avoid psyllium entirely.

Intestinal Obstruction or Risk of Obstruction
Why it’s dangerous:
Psyllium absorbs water and expands significantly. In someone with existing or impending intestinal blockage, adding bulk can worsen or complete the obstruction.
Includes:
- Diagnosed intestinal obstruction
- Symptoms suggesting obstruction (severe pain, vomiting, inability to pass gas).
- History of intestinal narrowing (strictures).
- Previous partial bowel obstructions.
- Adhesions from surgery are causing narrowing.
What happens?
Psyllium can create a mass that completely blocks intestinal passage, requiring emergency medical intervention or surgery.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia).
Why it’s dangerous:
Psyllium forms a thick gel rapidly. People with swallowing difficulties risk choking or aspirating the gel into their lungs.
Includes:
- Diagnosed dysphagia from any cause.
- Esophageal strictures or narrowing.
- History of choking episodes.
- Neurological conditions affecting swallowing (stroke, Parkinson’s, ALS).
- Throat surgery affecting swallowing.
What happens?
The gel can lodge in the throat or esophagus, creating complete airway obstruction or severe respiratory distress.
Known Psyllium Allergy.
Why it’s dangerous:
Allergic reactions to psyllium, though rare, can be severe and potentially life-threatening.
Symptoms of allergy:
- Skin rash, hives, or itching.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Anaphylaxis (severe, life-threatening reaction).
Risk factors for allergy:
- Healthcare workers with occupational exposure to psyllium powder.
- People with multiple food allergies.
- History of severe allergic reactions.
If you’ve ever had an allergic reaction to psyllium, it’s an absolute psyllium husk contraindication – never use it again.
Fecal Impaction.
Why it’s dangerous:
Existing fecal impaction means stool is already lodged and blocking the colon. Adding more bulk worsens the problem.
Symptoms suggesting impaction:
- No bowel movement for week+ despite urge.
- Small liquid stool leaking around a hard mass.
- Severe lower abdominal pain.
- Inability to pass gas.
- Rectal pain or bleeding.
What to do:
Seek medical treatment for impaction before ever considering fiber supplementation.
Relative Psyllium Husk Contraindications Requiring Medical Supervision.
These conditions don’t automatically preclude psyllium use, but require caution and medical oversight.

Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis:
During active flares, fiber can worsen symptoms and pain. However, during remission, some IBD patients benefit from psyllium.
Guidelines:
- Never use during active flare.
- Only introduce during confirmed remission.
- Start with very small amounts (1/4 teaspoon).
- Requires gastroenterologist approval.
- Monitor closely for symptom changes.
Diverticulitis.
During an acute episode:
Complete psyllium husk contraindication. Active inflammation requires a low-fiber or liquid diet.
During remission:
Psyllium helps prevent future episodes by preventing constipation. Requires medical guidance.
Key distinction:
Diverticulosis (pockets present but not inflamed) often benefits from psyllium. Diverticulitis (active inflammation) absolutely requires avoiding fiber.
Gastroparesis.
Why caution is needed:
Delayed stomach emptying means food and fiber sit in the stomach longer. Psyllium could worsen nausea, bloating, and discomfort.
If approved by the doctor:
- Use minimal amounts (1/4 -1/ 2 teaspoon).
- Mix very thoroughly with ample liquid.
- Monitor symptoms closely.
- May need to avoid entirely if symptoms worsen.
Previous Gastrointestinal Surgery.
Surgeries requiring caution:
- Gastric bypass or other bariatric surgery.
- Bowel resection.
- Colostomy or ileostomy.
- Any surgery creating strictures or altered anatomy.
Why it matters:
Changed anatomy might create areas where fiber could accumulate or cause obstruction.
Approach:
- Requires surgeon approval before starting psyllium.
- May need modified doses.
- Close monitoring is essential.
Esophageal Disorders.
Conditions requiring caution:
- Esophageal stricture (narrowing).
- Achalasia (swallowing disorder).
- Severe GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease).
- Barrett’s esophagus.
Concerns:
Psyllium gel could lodge in narrowed areas or worsen reflux symptoms.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding.
Generally safe but requires medical clearance:
While psyllium is considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, you should still consult your healthcare provider before starting.
Special considerations:
- Ensure adequate hydration (even more critical during pregnancy).
- Monitor for any unusual symptoms.
- Adjust dose conservatively.
- Take away from prenatal vitamins (2-4 hours separation).
Medication Interactions: Critical Psyllium Husk Contraindications.
Psyllium can reduce the absorption of certain medications, making this a significant psyllium husk contraindication concern when timing isn’t properly managed.
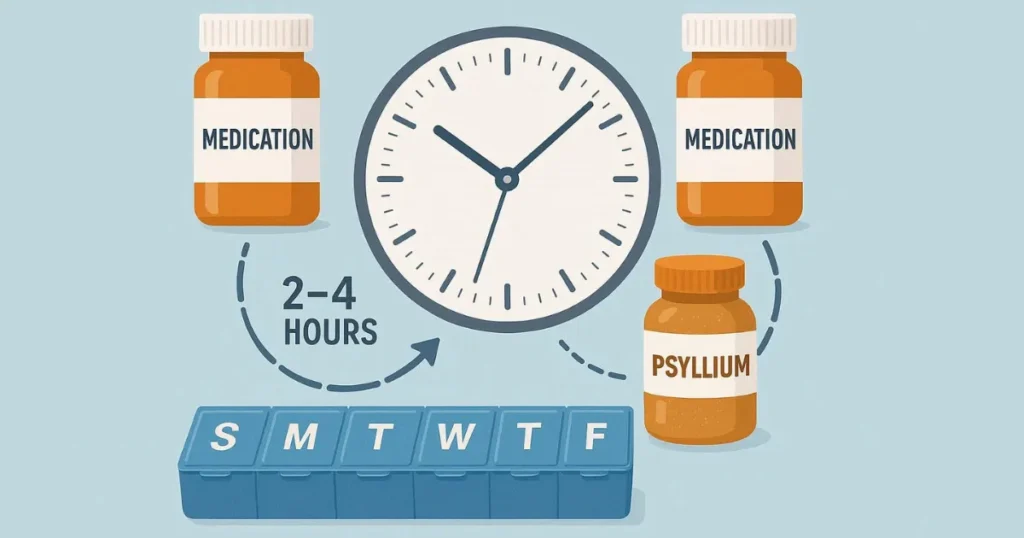
Medications Requiring Separation.
Take psyllium 2-4 hours away from these medications:
Diabetes medications:
- Metformin.
- Insulin.
- Sulfonylureas.
- Other blood sugar medications.
Concern: Psyllium slows carbohydrate absorption, potentially enhancing blood sugar lowering effects unpredictably.
Thyroid medications:
- Levothyroxine (Synthroid).
- Other thyroid hormones.
Concern: Psyllium can bind to thyroid medication, reducing absorption by 20-30%.
Heart medications:
- Digoxin.
- Beta-blockers.
- Some blood pressure medications.
Concern: Reduced medication absorption could lead to uncontrolled heart conditions.
Antidepressants:
- Tricyclic antidepressants.
- Some SSRIs.
Concern: Psyllium may reduce effectiveness, worsening mental health symptoms.
Lithium:
Psyllium can reduce lithium absorption, potentially destabilizing bipolar disorder.
Warfarin and blood thinners:
While not a complete contraindication, close monitoring of INR (blood clotting) is essential.
Cholesterol medications:
Interestingly, psyllium enhances statin effectiveness, but timing still matters for consistency.
How to Manage Medication Interactions.
The 2-4 hour rule:
- Take medications first.
- Wait 2-4 hours.
- Then take psyllium.
- OR reverse the order.
Example schedule:
- 7 AM: Morning medications.
- 11 AM: Psyllium dose.
- 6 PM: Evening medications.
- 10 PM: Psyllium dose (if taking twice daily).
Never consider medication interactions as a reason to avoid psyllium entirely – proper timing eliminates most concerns.
Special Populations Requiring Caution.
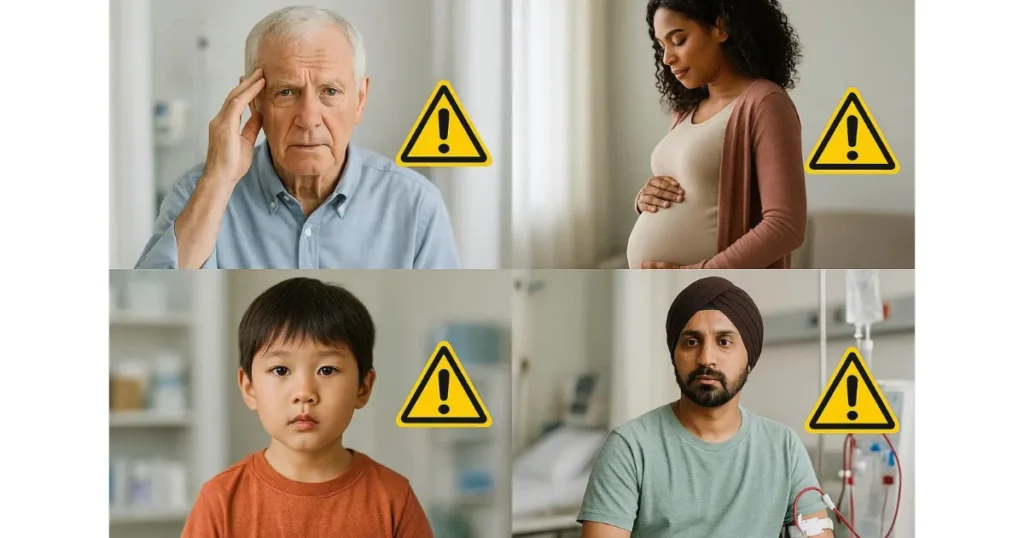

Elderly Individuals.
Why caution is needed:
- Reduced thirst sensation increases dehydration risk.
- More likely to have swallowing difficulties.
- Often take multiple medications.
- Higher risk of intestinal issues.
Safe approach:
- Start with very small amounts (1/4 -1/ 2 teaspoon).
- Emphasize hydration even more.
- Ensure ability to swallow safely.
- Review all medications with the doctor.
Children Under 6 Years.
Why it’s cautious:
- Limited safety data for very young children.
- Higher choking risk.
- Difficulty ensuring adequate hydration.
- Immature digestive systems.
Approach:
- Requires pediatrician approval.
- Generally recommended only for ages 6+.
- If approved, use half doses with careful supervision.
People with Kidney Disease.
Why caution matters:
While psyllium doesn’t directly harm kidneys, adequate hydration is crucial and can be complex with kidney disease.
Concerns:
- Fluid restrictions in advanced kidney disease.
- Electrolyte imbalances.
- Medication interactions (many kidney patients take multiple drugs).
Requires:
Nephrologist approval and guidance on safe hydration levels.
Warning Signs to Stop Psyllium Immediately.
Even without formal contraindications, certain symptoms indicate psyllium isn’t working for you.

Severe Symptoms Requiring Medical Attention.
Stop psyllium and seek immediate care if:
- Severe, persistent abdominal pain.
- Vomiting, especially if unable to keep liquids down.
- No bowel movement for 3+ days despite psyllium.
- Difficulty breathing or chest tightness.
- Severe allergic reaction symptoms.
- Blood in stool (more than small streaks).
- Signs of intestinal obstruction.
Moderate Symptoms Requiring Dose Adjustment or Discontinuation.
Stop or reduce psyllium if experiencing:
- Worsening constipation instead of improvement.
- Persistent bloating and discomfort beyond 2 weeks.
- Difficulty swallowing or choking sensation.
- Persistent nausea.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- New or worsening digestive symptoms.
Contact your healthcare provider to discuss whether psyllium is appropriate for you.
How to Discuss Psyllium Husk Contraindications with Your Doctor.
Questions to Ask.
Before starting psyllium:
- “Given my medical conditions, are there any psyllium husk contraindications I should know about?”
- “How should I time psyllium with my current medications?”
- “What symptoms should I watch for that would indicate I should stop?”
- “What dose do you recommend I start with?”
- “How often should I follow up regarding psyllium use?”
Information to Provide.
Tell your doctor about:
- All medications and supplements you take.
- All medical conditions, especially digestive issues.
- Any previous adverse reactions to fiber supplements.
- Current digestive symptoms.
- Upcoming surgeries or procedures.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding status.
Comprehensive disclosure helps your doctor identify any psyllium husk contraindications specific to you.
Quality Considerations and Safety.
The quality of psyllium affects safety and tolerability.

Why Quality Matters for Safety.
Premium psyllium (Pakistani sources):
- 85-99% purity reduces impurities that might cause reactions.
- Finer particle size reduces choking risk.
- More consistent results mean more predictable effects.
- Better quality control reduces contamination risk.
Lower-grade psyllium:
- May contain more plant matter or fillers.
- Coarser particles are harder to swallow safely.
- Variable results make monitoring difficult.
- Higher risk of contamination.
When psyllium husk contraindications exist, quality becomes even more critical. If you have relative contraindications requiring medical supervision, using premium psyllium from sources like Malik Psyllium provides the consistency and purity needed for safe, monitored use.
Common Myths about Psyllium Contraindications.
Myth 1: “Everyone Can Use Psyllium Safely”.
Reality: While safe for most people, real psyllium husk contraindications exist that make it dangerous for some individuals.
Myth 2: “Natural Means No Contraindications”.
Reality: Natural substances can still have significant contraindications and interactions. “Natural” doesn’t equal “safe for everyone.”
Myth 3: “Psyllium Contraindications Only Apply to People with Digestive Issues”.
Reality: Medication interactions, swallowing disorders, and allergies are equally important contraindications unrelated to primary digestive health.
Myth 4: “If I Take Psyllium Away from Food, Medication Interactions Don’t Matter”.
Reality: Timing separation from medications is essential, but food timing doesn’t eliminate medication interactions.
What are the main psyllium husk contraindications?
Absolute contraindications include intestinal obstruction, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), known psyllium allergy, and fecal impaction. Relative contraindications include active IBD, diverticulitis, gastroparesis, and certain medications.
Can I take psyllium with diabetes medication?
Yes, but take psyllium 2-4 hours away from diabetes medications. Psyllium can enhance blood sugar lowering effects, requiring closer monitoring and potential medication adjustment.
Is psyllium contraindicated with thyroid medication?
Not absolutely contraindicated, but requires a 2-4 hour separation. Psyllium can reduce levothyroxine absorption by 20-30% if taken simultaneously, affecting thyroid control.
Who should not take psyllium husk?
People with swallowing difficulties, intestinal obstruction, psyllium allergy, or acute fecal impaction should not take psyllium. Those with IBD, diverticulitis, or gastroparesis require medical supervision.
Are there psyllium husk contraindications during pregnancy?
Psyllium is generally safe during pregnancy, but consult your doctor first. Ensure adequate hydration and take away from prenatal vitamins to prevent nutrient absorption interference.
What medications interact with psyllium?
Thyroid hormones, diabetes medications, digoxin, some antidepressants, lithium, and blood thinners interact with psyllium. Take psyllium 2-4 hours away from all medications.
Can elderly people safely use psyllium?
Yes, with caution. Elderly individuals need careful dose titration, emphasis on hydration, swallowing ability assessment, and medication interaction review before starting psyllium.
Is psyllium safe with kidney disease?
Requires nephrologist approval. Fluid restrictions in advanced kidney disease can complicate proper psyllium hydration. Medication interactions are also more complex with kidney disease.
Conclusion.
Understanding psyllium husk contraindications ensures you use this beneficial fiber safely and effectively. Absolute contraindications – intestinal obstruction, severe swallowing difficulties, known psyllium allergy, and acute fecal impaction – require complete avoidance. Relative contraindications, including IBD during flares, active diverticulitis, gastroparesis, and certain surgeries, require medical supervision but don’t necessarily prevent use during appropriate circumstances. Medication interactions represent critical psyllium husk contraindications that demand proper timing – maintaining a 2-4 hour separation between psyllium and medications like thyroid hormones, diabetes drugs, heart medications, and antidepressants prevents reduced drug effectiveness.
Special populations, including elderly individuals, young children, pregnant women, and those with kidney disease, require extra caution and medical consultation before starting psyllium. Warning signs like severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, worsening constipation, or allergic symptoms indicate immediate discontinuation and medical evaluation. Quality significantly impacts safety – premium Pakistani psyllium with 85-99% purity from sources like Malik Psyllium provides consistency crucial for monitored use in people with relative contraindications.
The majority of people can safely use psyllium with proper hydration and technique, but respecting genuine contraindications prevents serious complications. Always consult healthcare providers before starting psyllium if you have significant medical conditions, take multiple medications, or have concerns about potential contraindications. Comprehensive disclosure of your medical history helps identify any psyllium husk contraindications specific to you, allowing informed decisions about whether this powerful fiber supplement suits your individual health circumstances and needs.
Malik Shabbir
Featured Blogs

Isabgol Ke Fayde – Psyllium Husk Ke Poori Science-Based Rahnumayi – 2026
Isabgol ke fayde jaanna aaj ke daur mein zyada zaroori

Isabgol Benefits in Hindi | Psyllium Husk Ke Fayde, Sahi Upyog Aur Savdhaniyan – 2026
Agar aap isabgol benefits in hindi mein samajhna chahte hain,
